
There can be problems from having a pacemaker placed in your chest. 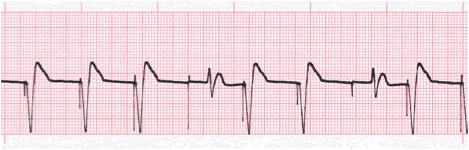 A pacemaker sends electrical pulses to your heart to help it work better. For example, a pacemaker may help you if your heart's ventricles don't pump at the same time. Talk to your doctor about the reasons that you might want one. Heart experts have guidelines about who might benefit from a pacemaker. This includes eating healthy foods that are low in salt, and not smoking. You'll also need to follow a healthy lifestyle to help treat heart failure. If you get a pacemaker, you still need to take medicines for heart failure. It may help keep you out of the hospital and help you live longer. A pacemaker can slow down the progression of heart failure. A pacemaker for heart failure, also called cardiac resynchronization therapy or CRT, can help you feel better so you can do your daily activities. This type of programming is therefore not suitable for patients with very high pacing thresholds that can exceed 5 Volts per 1 ms. The minimum pulse duration for the atrial threshold control is 0.4 ms, the maximum amplitude that can be delivered is 5 Volts per 1 ms and the minimum amplitude is 1 Volt for 0.4 ms. Once the threshold measurement is achieved, the device can adapt the output amplitude for the following 24 hours. A loss of atrial capture is demonstrated in the absence of ventricular sensing in the expected window. The AV conduction method (AVC) is applied in patients with preserved AV conduction (1:1 conduction after atrial pacing with fixed AP-VS intervals at a given rate). The diagnosis of loss of capture is thus made on the sensing of spontaneous atrial signals. If no spontaneous atrial event is sensed, the device concludes to an effective atrial capture. If the atrial pacing is not effective (absence of capture), the sinus node is not reset, which results in a reappearance of the spontaneous atrial activity. If the atrial pacing is effective, the sinus activity is inhibited. Atrial Chamber Reset (ACR) is used to assess the capture by observing the response of the intrinsic rhythm to an atrial pacing that is faster than the spontaneous rhythm of the patient.
A pacemaker sends electrical pulses to your heart to help it work better. For example, a pacemaker may help you if your heart's ventricles don't pump at the same time. Talk to your doctor about the reasons that you might want one. Heart experts have guidelines about who might benefit from a pacemaker. This includes eating healthy foods that are low in salt, and not smoking. You'll also need to follow a healthy lifestyle to help treat heart failure. If you get a pacemaker, you still need to take medicines for heart failure. It may help keep you out of the hospital and help you live longer. A pacemaker can slow down the progression of heart failure. A pacemaker for heart failure, also called cardiac resynchronization therapy or CRT, can help you feel better so you can do your daily activities. This type of programming is therefore not suitable for patients with very high pacing thresholds that can exceed 5 Volts per 1 ms. The minimum pulse duration for the atrial threshold control is 0.4 ms, the maximum amplitude that can be delivered is 5 Volts per 1 ms and the minimum amplitude is 1 Volt for 0.4 ms. Once the threshold measurement is achieved, the device can adapt the output amplitude for the following 24 hours. A loss of atrial capture is demonstrated in the absence of ventricular sensing in the expected window. The AV conduction method (AVC) is applied in patients with preserved AV conduction (1:1 conduction after atrial pacing with fixed AP-VS intervals at a given rate). The diagnosis of loss of capture is thus made on the sensing of spontaneous atrial signals. If no spontaneous atrial event is sensed, the device concludes to an effective atrial capture. If the atrial pacing is not effective (absence of capture), the sinus node is not reset, which results in a reappearance of the spontaneous atrial activity. If the atrial pacing is effective, the sinus activity is inhibited. Atrial Chamber Reset (ACR) is used to assess the capture by observing the response of the intrinsic rhythm to an atrial pacing that is faster than the spontaneous rhythm of the patient. 
Otherwise, the device selects the AV conduction method (AVC). If the patient's sinus rhythm is normal and stable, the device automatically selects the Atrial Chamber Reset (ACR) method. Before initiating a pacing threshold search, the pacemaker evaluates whether the patient is paced at the atrial level or whether there is a slow-rate sensing of sinus activity. The atrial threshold measurement is not based on the analysis of the evoked atrial response but rather on the highlighting of spontaneous atria or ventricles (2 methods depending on the presence or absence of atrioventricular conduction).


#A paced with failure to capture verification#
The atrial Auto-threshold model was also favored, the atrial threshold being measured periodically (a single daily measurement at 1:00 am) with the amplitude adjustment as a function of this measurement for the next 24 hours without cycle to cycle verification of capture efficiency. There are a number of similarities with the functioning of the automatic ventricular threshold but also certain differences. This tracing raises the issue of the programming of the automatic adjustment of the atrial pacing amplitude.Īs with the ventricular channel, it is possible to program an automatic measurement of the atrial threshold with automatic adjustment of the programming. In a second instance, the pacing threshold stabilized around 1.6 Volts for 0.4 ms allowing long-term programming at 2.8 Volts for 0.4 ms thus ensuring an acceptable safety margin and consumption. Increasing the output amplitude to 4 volts for 0.4 ms resolved the problem. The sensing remained correct (> 2 mV) and the pacing impedance normal (500 ohms). Without an identifiable cause, the pacing threshold had passed beyond this value (threshold at 3 Volts for 0.4 ms). Atrial output amplitude was programmed in this patient at 2.5 volts for a pulse duration of 0.4 ms. This tracing reveals a failure of atrial capture.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
